In December 2020, Kobe Steel announced that it supports the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and decided to join the TCFD Consortium, an organization of TCFD supporter organizations in Japan.


The KOBELCO Group recognizes CO2 reduction as a top management priority. As such, we announced our aim to increase corporate value through a transition to carbon neutrality that we aim to achieve by 2050 in the KOBELCO Group MediumTerm Management Plan (fiscal 2021–2023) announced in May 2021.
Going forward, the KOBELCO Group will continue to pursue reduction of CO2 emissions in order to contribute to realization of “a world in which people, now and in the future, can fulfill their hopes and dreams while enjoying safe, secure, and prosperous lives” as envisioned in KOBELCO’s View of the Future.
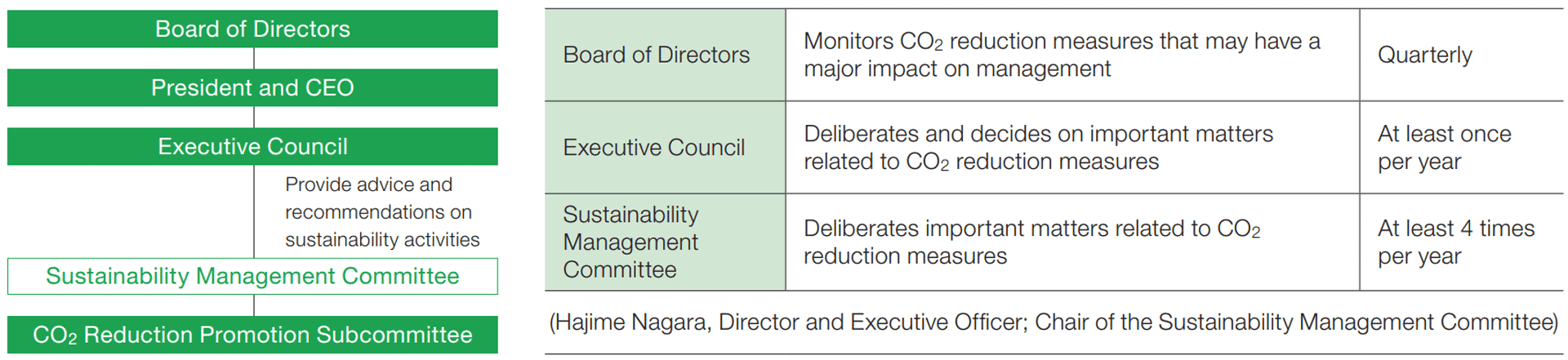
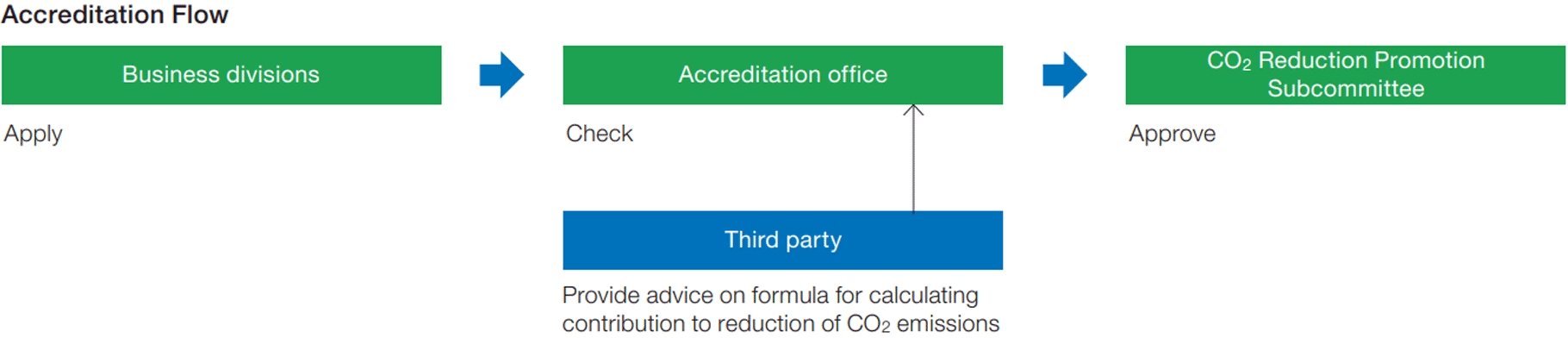
We established the CO2 Reduction Promotion Subcommittee under the Sustainability Management Committee (chaired by a director and executive officer) as an organization that specializes in dealing with issues related to the risks and opportunities associated with climate change. The subcommittee, tasked with conducting strategic reviews of climate change, studies and implements Companywide activities to address the risks and opportunities of climate change.
Assessment and management of climate-related risks and opportunities are regarded as important management issues, and important decisions of the CO2 Reduction Promotion Subcommittee are subject to the approval of the relevant Executive Steering Committee. The Steering Committee consists of directors and executive officers, as knowledge from a wide range of perspectives and viewpoints is required for climate-related issues, including business, management, legal, and technological development.
The activities of the CO2 Reduction Promotion Subcommittee and its study outcomes are reported through the Sustainability Management Committee to the Board of Directors quarterly for supervision and guidance from the Board of Directors. Important decision-making related to climate change involves a system of direct governance by senior management. Under this system, recommendations are made to the Executive Council through the Sustainability Management Committee, with the matter then approved by the President and CEO or a resolution of the Board of Directors following deliberation by the Executive Council.
The KOBELCO Group analyzes the medium- to long-term risks and opportunities associated with climate change considering various guidelines, including the social scenarios presented by the International Energy Agency; the long-term visions formulated and announced by the Japan Iron and Steel Federation, the Japan Aluminium Association, and other industry organizations; and the energy policies of Japan. Based on the analysis results, we evaluate the appropriateness of our Group’s activities.
Innovative technology to reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 20% from blast furnace operations successfully verified
The Group successfully demonstrated the technology that can reduce a significant amount of CO2 emissions from blast furnace operations, combining the MIDREX® technologies in the engineering business and the blast furnace operation technology in the iron and steel business. This achievement is a result of the integrated efforts of the KOBELCO Group leveraging its diverse businesses.
The quantity of CO2 emissions from the blast furnace is determined by the reducing agent rate (RAR)1, namely the quantity of carbon fuel used in blast furnace ironmaking. In the demonstration test, it was verified that RAR could be stably reduced from 518 kg/tHM (ton hot metal) to 415 kg/tHM by charging a large amount of hot briquetted iron (HBI) produced by the MIDREX® Process. The results indicate that this technology can reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 20% compared to a conventional method2.
In addition, the world’s lowest level of coke rate (239 kg/tHM) has been achieved in the demonstration test of this technology. The Company sees it as a promising solution that could become readily available in the near future at a lower additional cost compared to other CO2 reduction measures.
The key technologies that led to this achievement are two proprietary technologies developed by the KOBELCO Group, which are commonly available for other companies’ blast furnaces.
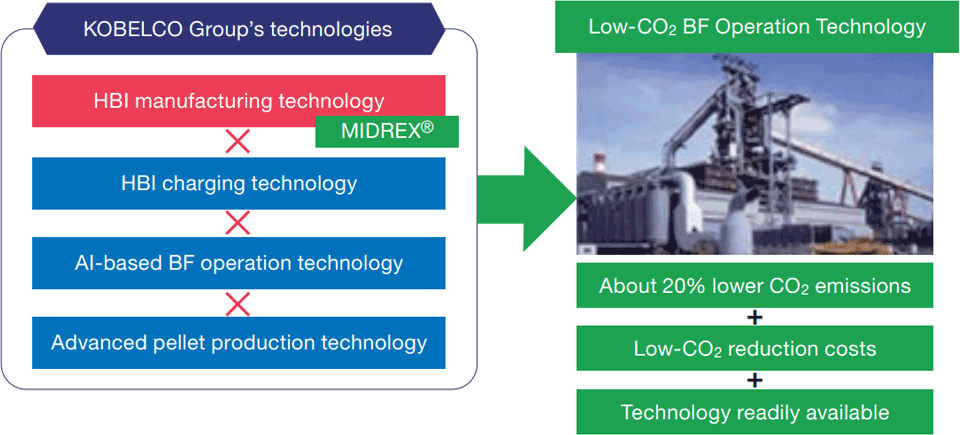
We will continue striving to further improve our low-CO2 blast furnace operation technology to further reduce CO2 emissions and lower CO2 reduction costs, thereby reducing our own CO2 emissions. Based on the aforementioned solution, we will help accelerate CO2 reduction through promoting HBI charging in blast furnaces around the world.
1 Coke rate (determined by the quantity of coke used in blast furnace) + pulverized coal rate (determined by the quantity of pulverized coal injected into blast furnace)
Coke is a carbon fuel made from coal, and pulverized coal is coal crushed to a powder.
2 The results are compared with fiscal 2013, which is the base year of the CO2 reduction targets set by the government and the KOBELCO Group.
Detail is below:
According to the “Mandatory Greenhouse Gas Accounting and Reporting System (published by the Ministry of the Environment)” Kobe Steel is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases in Japan. Our Company pays the carbon tax, Tax for Climate Change Mitigation (289 yen per ton of CO2 emissions from the use of coal, oil, LPG, and LNG), and in the future, if the carbon tax is increased or new taxes are imposed with the introduction of carbon pricing, it is expected to have a significant impact on our business, so we are constantly monitoring these trends. If regulations or taxes are imposed on CO2 and other emissions in the future, our Group’s business activities, particularly those related to steel, will be restricted, which may have an impact on our Group’s business performance with a decrease in sales, an increase in costs, etc
The KOBELCO Group has been promoting energy conservation efforts as a measure to mitigate the impact of carbon pricing. Our Group invested approximately 0.55 billion yen in energy conservation capital investments in fiscal 2021.
One of the example of such investments in fiscal 2021 is the investment for the renewal of dust collectors and power transformers at the Saijo Plant. For other initiatives, please refer to “Initiatives to Save Energy and Reduce CO2 Emissions” on page 27.
In addition, the KOBELCO Group is engaged in the development of various technologies related to the reduction of CO2 emissions in production processes and contribution to reduction of CO2 emissions through technologies, products, and services in order to contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions by society as a whole. In fiscal 2021, we spent approximately 4.8 billion yen on research and development related to climate change.
In order to better understand future climate-related risks and opportunities, we carried out medium-term (2030) and longterm (2050) scenario analysis. Our scenario analysis is based on the International Energy Agency (IEA)’s 2°C scenario (SDS: Sustainable Development Scenario) and 1.5°C senario (Net Zero by 2050) as well as the 4°C senario presented by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in its Sixth Assessment Report. For our analyses and evaluations, we also refer to long-term visions published by industry organizations to which we belong, such as the Japan Iron and Steel Federation (JISF) and the Japan Aluminium Association. For the electric power business, which is closely related to Japan’s energy policy, we conduct scenario analysis based on the energy policy of the national government. We also regularly review our analysis and evaluation of risks and opportunities based on changes in the external environment.
As more than 90% of our Group’s CO2 emissions come from the steelmaking process, the medium- to long-term trends in the steel industry will have the greatest impact on our business. According to the “JISF Long-Term Vision for Climate Change Mitigation—A Challenge towards Zero-Carbon Steel,” there is a certain correlation between economic growth and the amount of steel stock per capita. Therefore, the demand for steel is expected to continue to increase along with the world’s economic growth and population growth.
Steel production can be broadly divided into production with natural resources (iron ore, mainly using blast furnaces and DRI) and production with reused scrap (mainly using electric arc furnaces). According to JISF predictions, the reuse of scrap is expected to increase significantly due to the increase in the total amount of steel stock. On the other hand, demand for steel cannot be met by reused scrap alone. Accordingly, production using natural resources (iron ore) will continue to require the same level of production as at present
Amid growing interest in the response to climate change and the disclosure of relevant information, the importance of CO2 reduction efforts in the iron and steel industry is expected to continue increasing. For this reason, we anticipate that our stakeholders, including national and local governments, investors, and customers, will pay greater attention to our efforts to reduce CO2 emissions from our own facilities and expand our environmental menu that contributes to CO2 reduction.
One of the KOBELCO Group’s core businesses is the manufacture and sale of steel products, which falls under the industry category of energy-intensive basic materials. The Group’s CO2 emissions in fiscal 2021 totaled 16.1 million tons (Scope 1 and Scope 2), which ranks high even in Japan’s manufacturing industry. Accordingly, we recognize that the trends of future national climate change policies, laws, and regulations, including carbon pricing, are transition risks that may have a significant impact on our business operations.
In May 2021, the KOBELCO Group announced, in its Medium-Term Management Plan (Fiscal 2021–2023), that it will take on the challenge of realizing carbon neutrality by 2050 and aim to increase corporate value through this transition. The KOBELCO Group has set targets for 2030 and a vision for 2050 from two angles: (1) reducing CO2 emissions in the Group’s own production processes, and (2) contributing to the reduction of CO2 emissions through the Group’s distinctive technologies, products, and services.
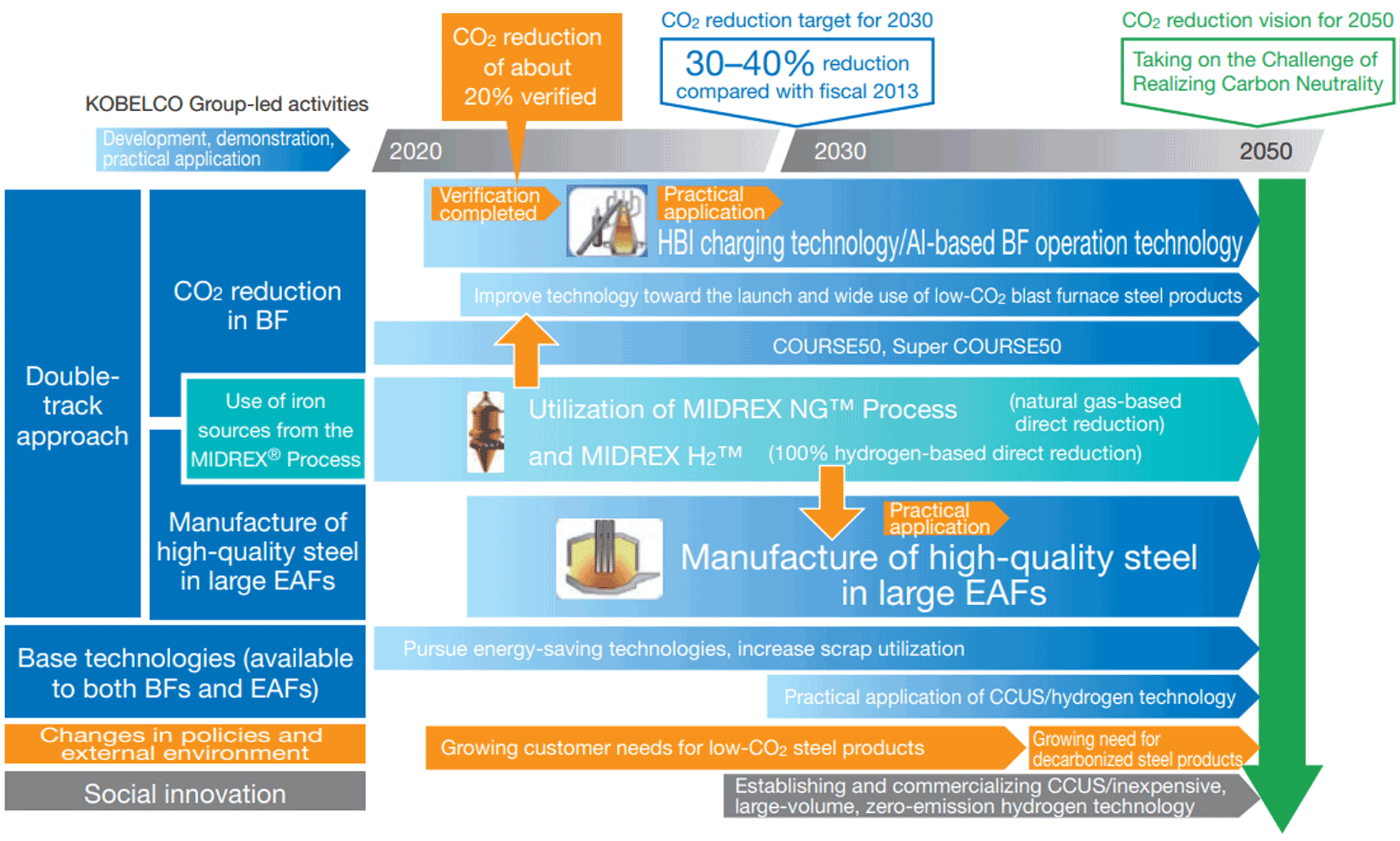
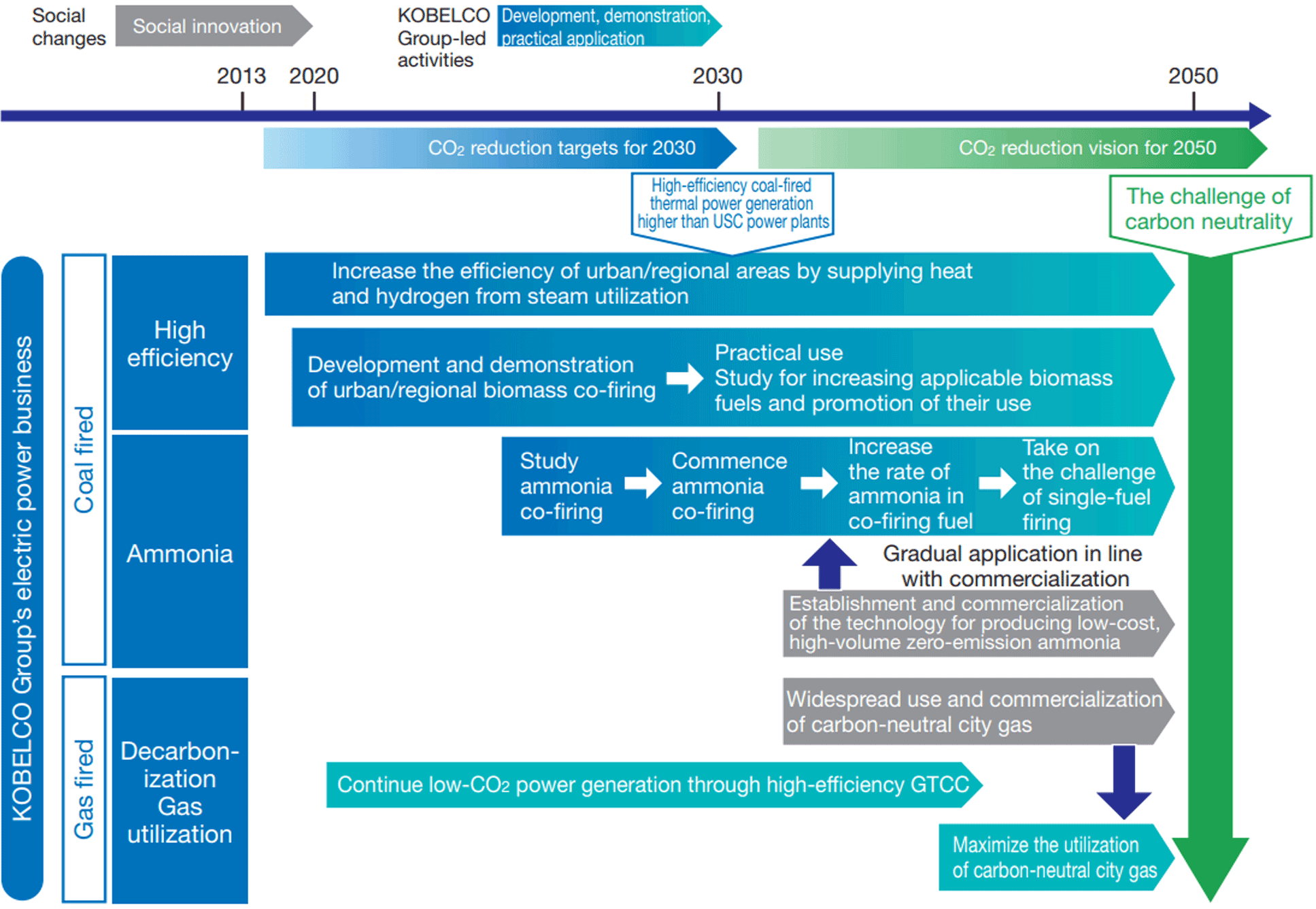
Regarding the reduction of CO2 emissions in our own production processes, we will promote CO2 reduction initiatives and mitigate risks by formulating roadmaps for carbon neutrality in the ironmaking processes and in the electric power business.
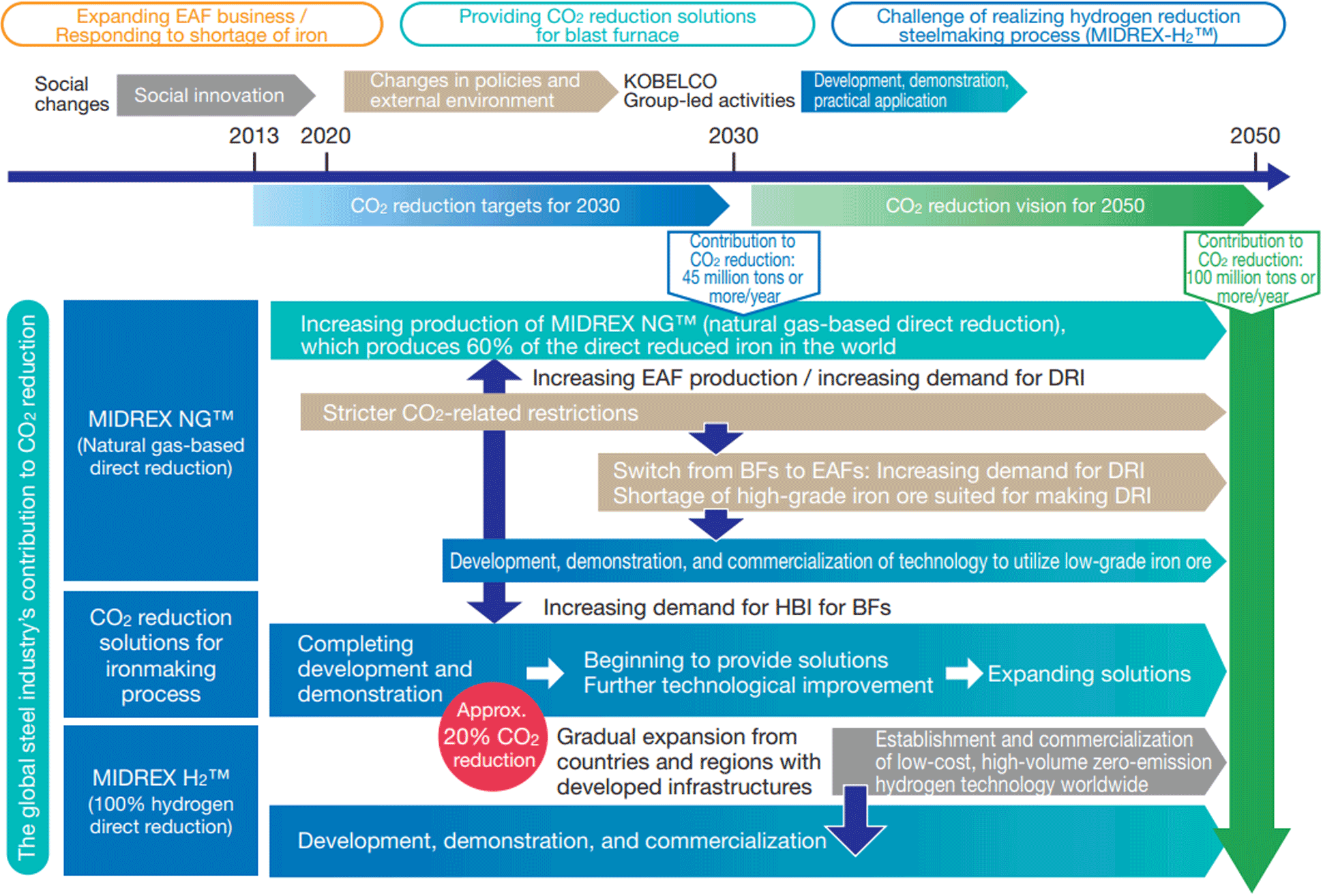
On the other hand, regarding the contribution to the reduction of CO2 emissions through the Group’s distinctive technologies, products, and services, we will make the most of opportunities by formulating a roadmap for the contribution to the reduction of CO2 emissions through the MIDREX® process.
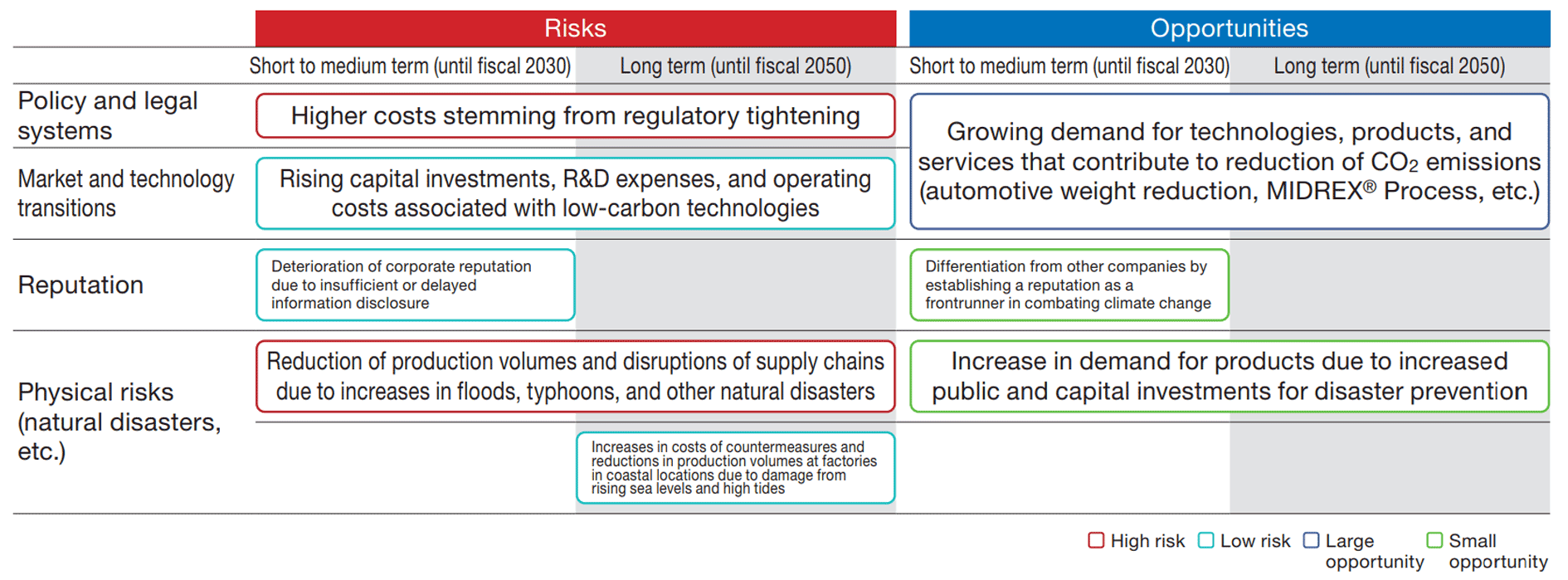
As for physical risks, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and various research institutes have reported that, as global warming progresses, the amount of precipitation tends to rise due to the increase of water vapor in the atmosphere, and damage caused by heavy rain and typhoons tends to become more severe. The risk of production stoppages and supply chain disruptions stemming from severe typhoons and heavy rains in recent years is also becoming more and more evident. The KOBELCO Group recognizes that further intensification of typhoons, floods, and other natural disasters caused by climate change poses a risk that could have a significant impact on its operations and lead to suspension of production activities.
In accordance with our Group’s Risk Management Regulations, we have defined “climate-related regulations” and “natural disaster preparation and recovery” as “Top Risks” that are expected to have a particularly severe impact when an event occurs, with the aim of strengthening our risk management.
As for opportunities, demand for low-CO2 products and services is increasing amid growing international interest in climate-related issues. We expect demand for products that help reduce CO2 emissions, such as our automotive weightreduction materials and the MIDREX® Process, to grow over the medium to long term.
Targets and Vision Announced in the KOBELCO Group Medium-Term Management (Fiscal 2021–2023)
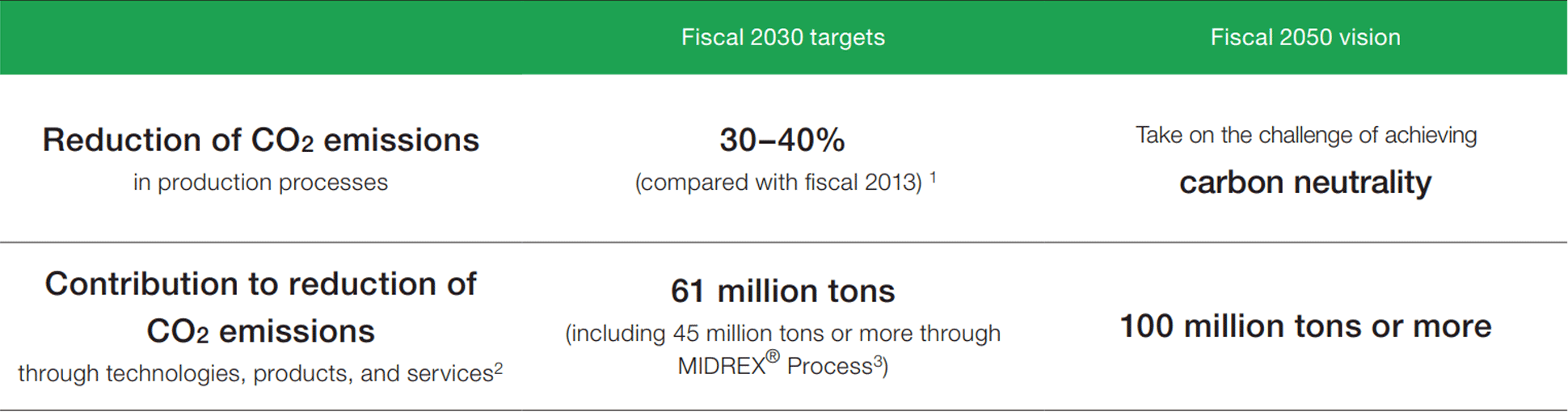
1 Most of the reduction targets are associated with iron and steel making processes. We reviewed the targets announced in September 2020 (with the change from Business As Usual (BAU) to the total amount basis, and the increased use of original solutions reflected)
2 The KOBELCO Group contributes to the reduction of CO2 emissions in various areas of society through its distinctive technologies, products, and services.
3 Reviewed calculation formula announced in September 2020
Roadmap for Carbon Neutrality in the Ironmaking Process
Roadmap for Carbon Neutrality in the Electric Power Business
Roadmap for CO2 Reduction through the MIDREX® Process
In regard to climate-related risks, we have identified (1) transition risks (policies and regulations) and (2) physical risks (preparations for and recovery from natural disasters) as Top Risks, which are risks that may have a material impact on the Group and its stakeholders and require a Groupwide response. We are working to strengthen risk management by appointing risk owners to each risk category.
Kobe Steel positions these two metrics as non-financial key performance indicators (KPIs) and manages them. Nonfinancial KPIs including CO2 reduction are discussed annually at the Executive Council as important items in the budget, and then they are discussed and approved by the Board of Directors.
In response to global warming, the KOBELCO Group promotes rationalization and research and development to reduce energy consumption throughout its operations in an effort to decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
In fiscal 2021, the KOBELCO Group’s businesses generated 16.1 million tons of CO2 emissions from energy use in total.
KOBELCO Group Worldwide CO2 Emission Data over the Past Three Years
| Unit | Fiscal 2019 | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 emissions from energy use (Scope 1 and 2) | Million t-CO2 | 16.5 | 15.3 | 16.1 |
| CO2 emissions from energy use (Scope 1) ✔ | Million t-CO2 | 15.6 | 14.5 | 15.3 |
| CO2 emissions from energy use (Scope 2) ✔ | Million t-CO2 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Net sales | Million yen | 1,869,835 | 1,705,566 | 2,082,582 |
| CO2 emission intensity from energy use per net sales | t-CO2 / Million yen | 8.8 | 9.0 | 7.7 |
| Products (crude steel, aluminum rolled products, copper rolled products) | Million t | 7.0 | 6.3 | 7.2 |
| CO2 emission intensity from energy use | t-CO2 / t-Product | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.2 |
* The data above covers 99% of the environmental impact of the KOBELCO Group. Emissions from offices are not included.
✔:Items covered by third-party assurance. In order to ensure the accuracy and transparency of energy consumption and CO2 emissions data, Kobe Steel receives a third-party assurance. For more information, please see the following:
Estimated Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Kobe Steel, Ltd.) (Scope 1)
| Item | Fiscal 2019 | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Energy-derived CO2 emissions*1 | 15,600,000 t-CO2 | 14,500,000 t-CO2 | 15,300,000 t-CO2 |
| 2. Non-energy derived CO2 emissions | 574,000 t-CO2 | 498,000 t-CO2 | 568,000 t-CO2 |
| 3. Methane (CH4) | 5,570 t-CO2 | 5,210 t-CO2 | 5,840 t-CO2 |
| 4. Nitrous oxide (N2O) | 43,600 t-CO2 | 49,600 t-CO2 | 6,610 t-CO2 |
| 5. Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) | 0 t-CO2 | 0 t-CO2 | 0 t-CO2 |
| 6. Perfluorocarbons (PFCs) | 0 t-CO2 | 0 t-CO2 | 0 t-CO2 |
| 7. Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) | 16,900 t-CO2 | 18,000 t-CO2 | 17,800 t-CO2 |
| 8. Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) | 0 t-CO2 | 0 t-CO2 | 0 t-CO2 |
1 Includes emissions of Group companies in and outside Japan
Kobe Steel, Ltd. Scope 3 emissions over the past three years (unit: thousand t-CO2)
| Category | Fiscal 2019 | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 | Calculation Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Purchased goods and services ✔ | 4,688 | 4,429 | 5,108 | The Company’s usage of main raw materials (annual amount of iron ore, coking coal, aluminum, and copper) multiplied by CO2 emissions unit values |
| 2. Capital goods ✔ | 263 | 262 | 113 | Capital investment cost multiplied by CO2 emissions unit values |
| 3. Fuel- and energy-related activities except scope 1 and 2 ✔ |
307 | 305 | 299 | Annual consumption of electricity, steam, fuel etc., multiplied by CO2 emissions unit values |
| 4. Upstream transportation and distribution ✔ |
192 | 180 | 217 | Using the calculation method for energy-derived CO2 emissions related to freight transportation by shippers as stipulated in the Act |
| 5. Waste generated in operations ✔ | 39 | 30 | 30 | The amount of industrial waste for each type multiplied by CO2 emissions unit values |
| 6. Business travel ✔ | 2 | 2 | 1 | Number of employees multiplied by CO2 emissions unit values |
| 7. Employee commuting ✔ | 5 | 5 | 5 | Number of employees multiplied by CO2 emissions unit values |
| 8. Upstream leased assets | N/A | N/A | N/A | CO2 emissions associated with the operation of assets leased to Kobe Steel are included in Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. |
| 9. Downstream transportation and distribution | N/A | N/A | N/A | We have no applicable business activities. |
| 10. Processing of sold products ✔ | 2,713 | 2,622 | 2,854 | Calculated by multiplying the production volume of main steel products by the CO2 emissions unit values at the time of processing each type of steel product. |
| 11. Use of sold products ✔ | 24,702 | 36,985 | 21,478 | Lifetime emissions for the main machinery products sold by the Company (energy used during use: electricity) are calculated based on units sold, expected average life, average power consumption, and CO2 emissions unit value for electricity. |
| 12. End-of-life treatment of sold products ✔ | 62 | 56 | 63 | Calculated by multiplying CO2 emissions unit values by the production volume of crude steel, aluminum, and copper products |
| 13. Downstream leased assets | N/A | N/A | N/A | We have no applicable business activities. |
| 14. Franchises | N/A | N/A | N/A | We do not have franchises. |
| 15. Investments | N/A | N/A | N/A | We have no applicable business activities |
| Total*3 ✔ | 32,972 | 44,876 | 30,168 |
1 Act on the Rational Use of Energy
2 As each category is rounded off to a whole number, the total of each category and the sum of categories 1 to 15 may not match.
✔ : Items covered by third-party assurance. In order to ensure the accuracy and transparency of energy consumption and CO2 emissions data, Kobe Steel receives a third-party assurance. For more information, please see the following:
In fiscal 2021, the KOBELCO Group worldwide used a total of 192 PJ of energy in all of its business divisions.
KOBELCO Group Worldwide Energy Data over the Past Three Years
| Unit | Fiscal 2019 | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy consumption ✔ | PJ | 196 | 182 | 192 |
| Net sales | Million yen | 1,869,835 | 1,705,566 | 2,082,582 |
| Energy intensity per net sales | GJ / Million yen | 105 | 107 | 92 |
| Products (crude steel, aluminum rolled products, copper rolled products) | Million t | 7.0 | 6.3 | 7.2 |
| Energy intensity per t-product | GJ / t-Product | 27.8 | 28.7 | 26.6 |
✔: Items covered by third-party assurance. In order to ensure the accuracy and transparency of energy consumption and CO2 emissions data, Kobe Steel receives a third-party assurance. For more information, please see the following:
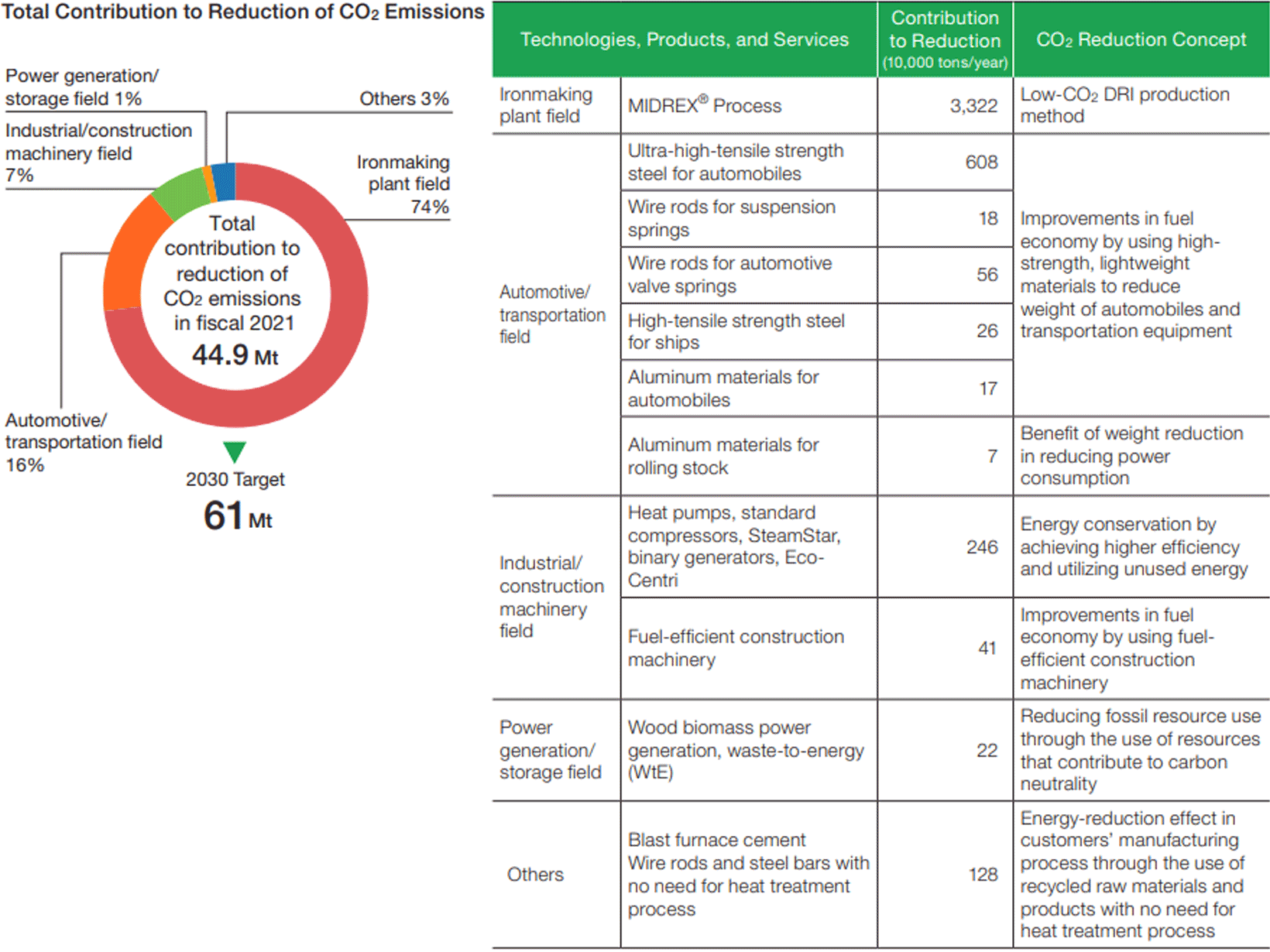
In May 2021, the KOBELCO Group announced, in its Medium-Term Management Plan (Fiscal 2021–2023), that it would take on the challenge of realizing carbon neutrality by 2050 and aim to increase corporate value through this transition. The KOBELCO Group has set targets for 2030 and a vision for 2050 from two angles: (1) reducing CO2 emissions in the Group’s own production processes, and (2) contributing to the reduction of CO2 emissions through the Group’s distinctive technologies, products, and services.
The Group has a variety of products and services that contribute to CO2 reduction. By expanding sales of these, we will contribute to the reduction of CO2 during use.
Other Major Technologies, Products, and Services That Contribute to CO2 Reductions (The amount of contribution will be calculated in the future.)
| Technologies, Products, and Services | Concept behind Reduction | |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive/transportation field | Fuel-cell separator materials, titanium for aircraft components | Improvement of fuel economy by reducing weight of automobiles and transportation equipment, effects of replacing gasoline-powered automobiles for next-generation vehicles |
| Hydrogen utilization field | High-purity Hydrogen Oxygen Generator (HHOG) | Effects of reducing fossil resource consumption through hydrogen utilization |
| Power generation/storage field | Conversion of sludge to fuel and its utilization at coalfired thermal power plants (planned) | Reducing fossil resource use through the use of resources that contribute to carbon neutrality |
| Initiatives for Implementation |
Long-Term Policies | Initiatives to Achieve Medium-Term Targets | Fiscal 2021 Results Self-assessment 〇: Progressing as planned △: Some issues remaining ×: Plan not achieved |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measures against global warming |
Contribute to preventing global warming by promoting energy conservation and CO2 reduction in all business activities <Target for 2030> Reduce CO2 emissions from production processes by 30- 40% (compared with fiscal 2013) <Vision for 2050> Taking on the challenge of achieving carbon neutrality |
Promote medium- to long-term technological development based on the roadmap and continue working on energy conservation initiatives, in order to achieve the targets for 2030 and vision for 2050 |
Implement initiatives and reviews following the Roadmap toward Carbon Neutrality in the Ironmaking Process and Power Generation Business. Fiscal 2021 results: 16% reduction (compared to fiscal 2013) |
〇 |
| Contributing to the environment through technologies, products, and services |
Create environmentally sustainable products and new businesses with due consideration to the environment in all technological and product development <Target for 2030> Contribution to CO2 emission reduction: 61 million tons (including at least 45 million tons of MIDREX®) <Vision for 2050> Contribution to CO2 emission reduction: 100 million tons or more |
Contribute to the creation of a low-carbon society through the efforts of the entire KOBELCO Group by working on issues related to the environment and energy fields, such as weight reduction of transportation vehicles, the creation of a hydrogen-based society, and the diversification of power sources |
Fiscal 2021 results: Contribution to CO2 reduction of 44.9 million tons |
〇 |
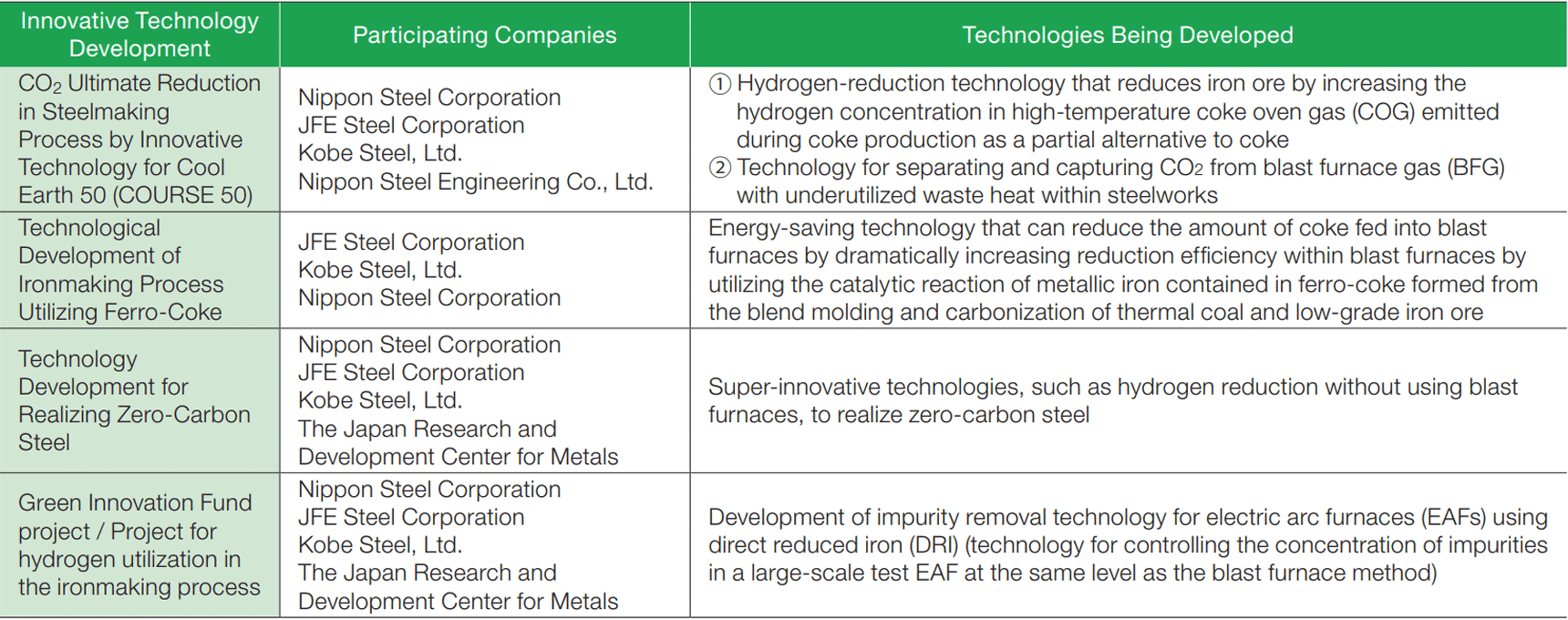
As a member of the Global CCS Institute and the Carbon Recycling Fund Institute, we actively acquire the latest information on Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technology and work on technological development and research on CO2 separation, capture, recycling, and sequestration for future practical use.
In addition, each of the following industry groups to which the KOBELCO Group belongs have formulated actions plans for carbon neutrality. We will contribute to the achievement of the targets set out in the action plans of each industry group to which we belong by pursuing energy savings and CO2 reduction in production processes.
| Industry Groups | Fiscal 2030 Industry Targets for Reducing CO2 Emissions from Production Processes in the Carbon Neutrality Action Plan |
|---|---|
| The Japan Iron and Steel Federation | 30% reduction compared to fiscal 2013 |
| Japan Aluminium Association | 31% reduction compared to fiscal 2013 |
| Japan Copper and Brass Association | Reduction of 6% energy intensity versus BAU* with production activity volume of 380,000 tons |
| The Japan Society of Industrial Machinery Manufacturers | Reduction of 10% in CO2 emissions versus fiscal 2013 |
| Japan Construction Equipment Manufacturers Association | Reduce the manufacturing energy consumption rate by 17% from the actual achievement of 2013. |
* Business As Usual (BAU): Emissions of greenhouse gases, or emissions per unit, assuming no additional measures are taken
In order to respond to climate change in a consistent manner, Kobe Steel has established a Groupwide governance system centered on the Sustainability Management Committee.
The Sustainability Management Committee informs and educates employees about our Group Corporate Philosophy, ESG policies, and various initiatives to ensure that employees fully understand our corporate policies concerning these matters
We collect information not only on the policies set by the Japanese government but also on industry targets and initiatives related to our business, as well as trends in regulations in the countries where we conduct business. Such information is shared with internal stakeholders, including directors and management.
When the KOBELCO Group engages in any activities that may influence the national government, local governments, industry associations, etc., all members of the Group shall report such activities to the Sustainability Management Committee in advance. The committee shall confirm whether such activities are consistent with the Group Corporate Philosophy and ESG policies. The committee shall report such activities to the Executive Council and the Board of Directors for oversight in accordance with the importance of such activities.
In addition, if the efforts of industry associations/groups are not in line with the Group Corporate Philosophy or ESG policies, Kobe Steel shall put forward its opinions to industry associations/groups and work to ensure that their initiatives are consistent with its policies.
| Production facility / company name | Location | Examples of initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Kakogawa Works, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Kakogawa, Hyogo Prefecture | Upgraded air compressors |
| Ibaraki Plant, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Ibaraki, Osaka Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Saijo Plant, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Higashihiroshima, Hiroshima Prefecture | Upgraded dust collectors Upgraded power transformers |
| Fukuchiyama Plant, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Fukuchiyama, Kyoto Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting Reduced load on electrical machinery through process improvements |
| Moka Plant, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Moka, Tochigi Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Chofu Works, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Shimonoseki, Yamaguchi Prefecture | Switched heat sources at certain buildings at plants |
| Daian Works, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Inabe, Mie Prefecture | Switched heat sources at certain buildings at plants |
| Kobe Corporate Research Laboratories, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture | Upgraded heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Takasago Works, Kobe Steel, Ltd. | Takasago, Hyogo Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Amagasaki Works, Shinko Wire Company, Ltd. | Amagasaki, Hyogo Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting Improved insulation performance of furnaces |
| Onoe Works, Shinko Wire Company, Ltd. | Kakogawa, Hyogo Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting Upgraded transformer |
| Nishikinohama Works, Shinko Wire Company, Ltd. | Kaizuka, Osaka Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Kobelco Compressors Corporation Harima Plant | Harima Town, Kako District, Hyogo Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting Upgraded boiler |
| Koshuha-Foundry Co., Ltd. | Hachinohe, Aomori Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting Upgraded high-voltage transformer to high-efficiency product |
| Harima Plant, Kobelco Eco-Solutions Co., Ltd. | Harima Town, Kako District, Hyogo Prefecture | Repaired air leaks |
| Shinko Industrial Co., Ltd. | Kurayoshi, Tottori Prefecture | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting Reduced the number of compressors |
| Kobelco Power Kobe Inc. | Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture | Reduced driving steam |
| Kobelco Spring Wire (Foshan) Co., Ltd. | China | Reused lubricant and heat insulation sand, and reduced power consumption by switching motor for turbulation of water treatment chemicals |
| Hangzhou Kobelco Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. | China | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Kobelco Precision Technology Sdn. Bhd. | Malaysia |
Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| Kobe Aluminum Automotive Products (KAAP) | United States | Used energy-efficient lighting |
| Kobelco Automotive Aluminum Rolled Products (China) Co., Ltd. | China | Used inverter-type compressor |
| Kobelco Singapore Kobelco Pte Ltd. | Singapore | Repaired air leaks |
| KOBELCO ALUMINUM PRODUCTS AND EXTRUSIONS INC. | United States | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
| KOBELCO MIG WIRE (THAILAND) Co., Ltd. | Thailand | Repaired air leaks |
| Thai-Kobelco Welding Co., Ltd. | Thailand | Upgraded chiller to inverter-type |
| Kobe Aluminum Automotive Products (China) Co., Ltd. | China | Switched a portion of plant lighting to LED lighting |
Kobe Steel, Ltd. has been responding to questionnaires from CDP* since fiscal 2009. Please refer to the following link for our response to the 2022 Climate Change Questionnaire.
* An international NGO that operates a global information disclosure system for managing environmental impacts. It sends environment-related questionnaires to companies and compiles the results to analyze and evaluate on a common scale.