Home > Press Releases > 2014 > Kobe Steel receives ClassNK special approval for the factor to calculate the design fatigue strength of built-up type crankshafts
Press Releases
The information on this Web site is presented "as is." Product availability, organization, and other content may differ from the time the information was originally posted. Changes may take place without notice.
![]()
 Kobe Steel receives ClassNK special approval for the factor to calculate the design fatigue strength of built-up type crankshafts
Kobe Steel receives ClassNK special approval for the factor to calculate the design fatigue strength of built-up type crankshafts
July 15, 2014
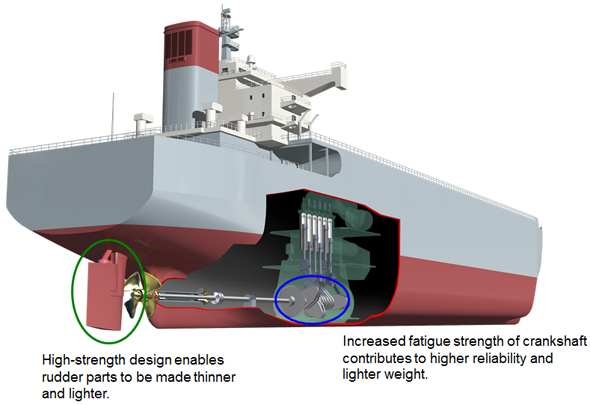
Kobe Steel, Ltd. has received special approval from the Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (also known as ClassNK or NK) for the factor to calculate the design fatigue strength of built-up type crankshafts for diesel engines in ships. Under the crankshaft design rules of the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS), Class NK has given 1.05 as the factor K for the calculation of the fatigue strength, the first time in the world by a ship classification society.
Making use of its expertise as an integrated manufacturer of steel forgings and incorporating techniques for clean steel, Kobe Steel has undertaken trials of its die-forging method that have successfully increased the fatigue strength of the crankshaft material by 20 percent compared with conventional forging methods.
ClassNK’s approval of higher design fatigue strength will guarantee higher reliability in the crankshaft as well as weight-savings that will contribute to improved fuel consumption.
With stricter regulations and requests to improve fuel consumption due to the high price of ship fuel, the need for “eco-ships” is rising. Two important points in the development of eco-ships are ship development to reduce drag on the hull and engine development to improve fuel consumption and lower exhaust gas emissions.
In engine development, ships are using larger propellers that rotate at slower speeds, driving the need for higher output at the lower rotating speed region. To meet this trend, long-stroke engines are growing in popularity. When long-stroke engines are used, the crank throws are longer and heavier than conventional ones, leading to higher load stress on the crankshaft and higher bearing loads.
In a separate development, Kobe Steel has increased the design strength of steel casting and forging materials for rudder parts by 60 percent, compared with conventional materials. These materials enable rudder stock and other casting parts to be made smaller and lighter, thereby increasing vessel speed and improving fuel consumption. These high-strength materials have already received approval from ship classification societies in various countries.
Responding to customer needs, Kobe Steel is contributing to the advancement of the shipping and shipbuilding industries.